Home Battery Storage: How to Choose the Right System for You
As energy demands increase and renewable energy becomes more widespread, more households are considering battery storage systems. Home battery storage systems not only provide backup power during outages but can also reduce electricity bills by storing low-cost power and improving energy independence. So, how do you choose the right home battery storage system? This article will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of different types of batteries, installation costs, government subsidies, and daily maintenance.

1. Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Types of Batteries
lithium battery
lithium batteries are currently the most common type of home storage battery because of their long lifespan, and relatively fast charge and discharge rates. Their advantages include:
High Energy Density: They take up little space, making them suitable for home installation.
Long Lifespan: They can generally be used for over 10 years with many charge-discharge cycles.
Low Maintenance: They require minimal daily maintenance.
However, the disadvantages of lithium-ion batteries should not be overlooked:
High Cost: The initial investment is significant.
Safety Concerns: There is a risk of overheating and fire, requiring a good management system.
Lead-Acid Cell
Lead-Acid Cells are a more traditional battery technology. Though the technology is relatively mature, they have a lower energy density and shorter lifespan. Their advantages include:
Low Cost: The initial investment is lower compared to lithium-ion batteries.
Mature Technology: There are many products available, and the technology is stable.
The disadvantages include:
Low Energy Density: They take up more space, which is not ideal for households with limited space.
Short Lifespan: Generally, they last 3-5 years and need frequent replacement.
High Maintenance Needs: They require regular maintenance and inspection.
Flow Batteries
Flow batteries, though not as common in the home storage market as lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries, have unique advantages:
Long Lifespan: They have a long cycle life and can undergo many charge-discharge cycles.
High Safety: They are less likely to overheat, making them safer.
Their disadvantages are also significant:
High Cost: Both initial investment and maintenance costs are high.
Large Space Requirement: They need large tanks for electrolyte storage, making them unsuitable for homes with limited space.
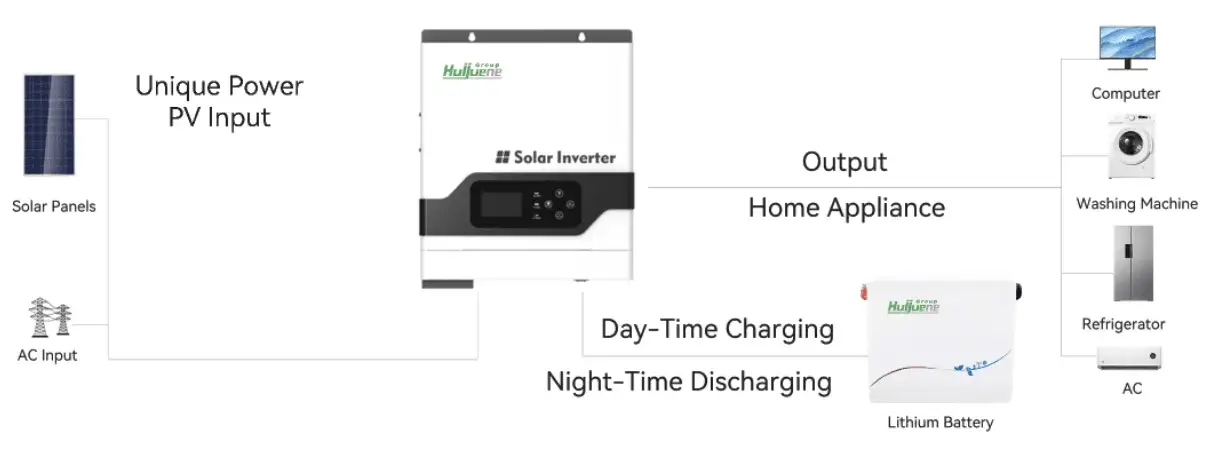
2. Installation Costs
The installation cost of home battery storage systems mainly includes equipment costs and installation fees. Equipment costs vary based on battery type, capacity, and brand. Generally, lithium-ion batteries are the most expensive, while lead-acid batteries are relatively cheaper. Flow batteries have the highest costs due to the need for additional storage tanks and complex management systems.
Installation fees depend on the difficulty of installation and labor costs in the area. When choosing a battery storage system, it is essential to consider both the equipment price and the overall installation cost to ensure the budget is manageable.
3. Government Subsidies
To encourage households to adopt clean energy, many countries and regions offer various government subsidies and tax incentives. Understanding and utilizing these policies can significantly reduce the investment cost of home battery storage systems. For example, the U.S. Federal Solar Tax Credit (ITC) can cover part of the installation costs of battery storage systems, while Germany offers the KfW loan program to help households install storage systems with low-interest loans.
Before choosing and installing a battery storage system, it is advisable to thoroughly understand the local subsidy policies and application processes to minimize costs.
4. Daily Maintenance
Daily maintenance of battery storage systems is crucial for extending their lifespan and ensuring stable operation. Different types of batteries have different maintenance needs:
Lithium-Ion Batteries: They require minimal daily maintenance but need periodic checks on the Battery Management System (BMS) and cooling system to prevent overheating and overcharging.
Lead-Acid Batteries: They require regular checks of the electrolyte levels and addition of distilled water as needed. Additionally, periodic equalization charging is necessary to prevent capacity decline.
Flow Batteries: Maintenance is more complex, requiring regular checks on the electrolyte condition and pump operation to ensure normal system function.
When choosing a battery storage system, understanding its maintenance needs and costs, and ensuring adequate technical support for effective management and maintenance, is essential for ensuring long-term stable operation.
Conclusion
Choosing the right home battery storage system requires a comprehensive consideration of battery type, installation costs, government subsidies, and daily maintenance. Although lithium-ion batteries have higher costs, their high energy density and long lifespan make them the preferred choice for many households. Lead-acid batteries are also a good option for those with limited budgets due to their lower cost and mature technology. Although flow batteries are expensive and take up a lot of space, their safety and long lifespan make them attractive in certain situations.
By understanding and utilizing government subsidy policies, you can significantly reduce installation costs. Regular maintenance and inspection of battery storage systems are also crucial for extending their lifespan and ensuring stable operation.
I hope this article provides valuable insights when choosing a home battery storage system and helps you find the best solution for your household.
