How to Evaluate the Return on Investment (ROI) of Power Storage Systems?
In the context of today’s energy transition, power storage systems are gradually becoming a hot topic in the energy sector. Whether to address the intermittency of renewable energy or to optimize electricity usage costs, many businesses and individuals are considering investing in power storage systems. However, before making a decision, it is crucial to accurately evaluate their return on investment (ROI).
Power storage systems are like giant energy “reservoirs” that can store excess electricity when there is a surplus and release it when needed. Common power storage technologies include lithium-ion batteries, lead-acid batteries, and flow batteries.

Key Points in Evaluating ROI
Cost Analysis
Equipment Purchase Cost
This is the primary expenditure of the investment, including core components such as battery packs, inverters, and control systems. Prices vary significantly depending on the type and specifications of the equipment, and are influenced by market supply and demand as well as technological advancements.
Installation Cost
This includes expenses for site preparation, wiring, and equipment installation and commissioning. Complex installation environments and high construction standards can increase these costs.
Maintenance Cost
During the entire lifespan of the system, regular maintenance and upkeep are required, such as battery balancing, equipment inspection, and repairs. Although relatively small, these costs should not be overlooked.
Replacement Cost
Components such as batteries have a finite lifespan and need replacement after expiration, representing an important long-term cost.
Revenue Calculation
Arbitrage on Peak and Off-Peak Electricity Prices
Understand local electricity pricing policies, particularly the difference between peak and off-peak prices. By charging during off-peak periods and discharging during peak periods, one can achieve arbitrage gains. For instance, if peak electricity price is 1.5 yuan/kWh and off-peak price is 0.5 yuan/kWh, charging 1000 kWh during off-peak and discharging during peak can yield a price difference gain of 1000 yuan.
Improving Power Reliability
For enterprises requiring high continuity of power supply, such as data centers and hospitals, power storage systems can provide backup power during outages, reducing losses. Although difficult to quantify in monetary terms, this is crucial for normal operations.
Participating in Power Market Services
In some regions, power storage systems can participate in ancillary services markets, such as frequency regulation and peak shaving, thereby earning corresponding remuneration.
Integrating Renewable Energy
When combined with solar or wind power generation facilities, excess generation can be stored, enhancing the utilization and value of renewable energy.
System Performance and Lifespan
Storage Capacity
The total amount of energy the system can store directly affects its usable scale and revenue potential.
Charge/Discharge Efficiency
Efficient charging and discharging processes can reduce energy losses, increasing the actual usable energy.
Cycle Life
The cycle life of the battery determines the overall lifespan of the system and the replacement cycle, thereby impacting costs and revenues.
Policies and Subsidies
Governments often introduce policies and subsidies to promote clean energy and storage technologies. Understanding and fully utilizing these policies and subsidies can significantly improve ROI.
Case Study
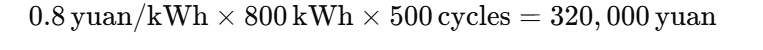
After deducting the annual maintenance cost of 50,000 yuan, the net annual revenue is 315,000 yuan.
Over the 10-year lifespan, the total revenue is 3,150,000 yuan. After deducting the initial investment of 2 million yuan, the ROI is: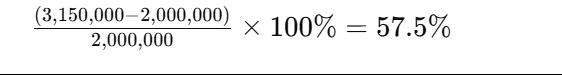
Of course, this is a simplified case, and actual situations need to consider more factors, such as battery performance degradation and policy changes.
Risks and Uncertainties
When evaluating the ROI of power storage systems, it is also necessary to fully consider risks and uncertainties.
Technological Advances
Rapid development in battery technology may lead to the early obsolescence of existing equipment or the emergence of new, more cost-effective technologies.
Electricity Price Fluctuations
Changes in electricity pricing policies and market supply and demand fluctuations can affect peak-off-peak price differences and arbitrage gains.
Equipment Failures
Although systems have a certain degree of reliability, equipment failures can still lead to unexpected repair and downtime costs.
In summary, evaluating the ROI of power storage systems requires comprehensive consideration of costs, revenues, system performance, policies, and other factors, along with a thorough understanding of potential risks and uncertainties. Only after a complete and in-depth analysis can wise investment decisions be made.
